

The meiotic spindle fibres attach to one chromosome of each pair.The centrioles are now at opposites poles of the cell with the meiotic spindles extending from them.The chromosome pairs line up next to each other along the centre (equator) of the cell.
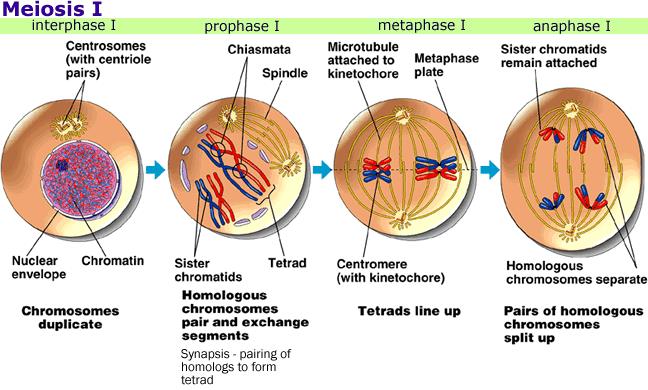
The meiotic spindle, consisting of microtubules and other proteins, extends across the cell between the centrioles.At the end of Prophase I the membrane around the nucleus in the cell dissolves away, releasing the chromosomes.The pairs of chromosomes may then exchange bits of DNA in a process called recombination or crossing over.The chromosomes pair up so that both copies of chromosome 1 are together, both copies of chromosome 2 are together, and so on.Each chromosome is composed of two sister chromatids containing identical genetic information.The copied chromosomes condense into X-shaped structures that can be easily seen under a microscope.During interphase, microtubules extend from these centrosomes.Outside of the nucleus are two centrosomes, each containing a pair of centrioles, these structures are critical for the process of cell division.

Crossing over during prophase i results in full#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
